All posts by saenzac
Oryx population example
I will show how to solve a classical problem of modeling a oryx population using differential equations. The problem says:
An African government is trying to come up with a good policy regarding the hunting of oryx. They are using the following model: the oryx population has a natural rowth rate of k years^-1, and there is assumed a constant harvesting rate of a oryxes/year. Tasks:
- Write down a model for the oryx population.
- Suppose a=0. What is the doubling time?
- Find the general solution of this equation.
- Check that the proposed solution satisfies the ODE.
- There is a constant solution. Find it.
- Graph the constant solution (equilibrium) and some others, Why, in this case, do we say the constant solution is “unstable”?
- growth rate:
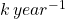
harvesting rate: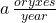
Let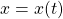 be the population of oryxes at time
be the population of oryxes at time 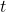 .
.
We can think as the change of oryxe population in a time interval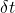 to be the result of the growth rate multiplied by the current population
to be the result of the growth rate multiplied by the current population 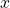 and by the time interval. And the decrease in population represented with a minus sign with the harvesting rate multiplied by the time interval. So we have:
and by the time interval. And the decrease in population represented with a minus sign with the harvesting rate multiplied by the time interval. So we have:
![]()
CREATE DB, dump and restore postgresql database
I will show how to create a new database (DB) with some user credentials and then a migration will be done. The migration consists of copying an entire database (DB) from one to another computer.
Creating a new DB:
The “openproject” database and a user of the same name are created. The user privileges are given to the new database and finally a password is set for the user.
$ sudo -u postgres psql $ postgres= create database openproject; $ postgres= create user openproject; $ postgres= grant all privileges on database "openproject" to openproject; $ postgres= alter user openproject with password 'new_password' ;
Then wen can make changes to the newly created database.
Create the backup with pg_dump command:
We make a backup of our “openproject” database with the following command. It include blobs, if any in our database.
$ pg_dump -h localhost -p 5432 -U postgres -F c -b -v -f <backup path> <database name>
-F c is custom format (compressed, and able to do in parallel with -j N)
-b is including blobs,
-v is verbose
-f is the backup file name
Restore the backup with
We can restore a previously backup database with the following command.
$ pg_restore -h localhost -p 5432 -U postgres -d -v <backup file name>
Just make sure the DB name is the same in both commands and that the destination DB is created before using pg_restore. And create the DB with the same user credentials as the original DB.
system identification using excel
In this article we will show how to do a third order system identification using excel. The identification takes place in the Laplace domain (![]() ) where the optimal system parameters are found by using the gradient descend method.
) where the optimal system parameters are found by using the gradient descend method.
Consider the following second order system, a DC motor for example:
![]()
Where ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() are the optimal parameters to be found by minimizing the cost function:
are the optimal parameters to be found by minimizing the cost function:

Transforming the system to the Z-domain by using Euler’s forward approximation:
![]()
Which leads to the following difference equations:
The cost function to be minimized is :
The validation shows a satisfactory match between the estimated and the real model:

$ls postfix.txt > Johnny
